Definition and Application
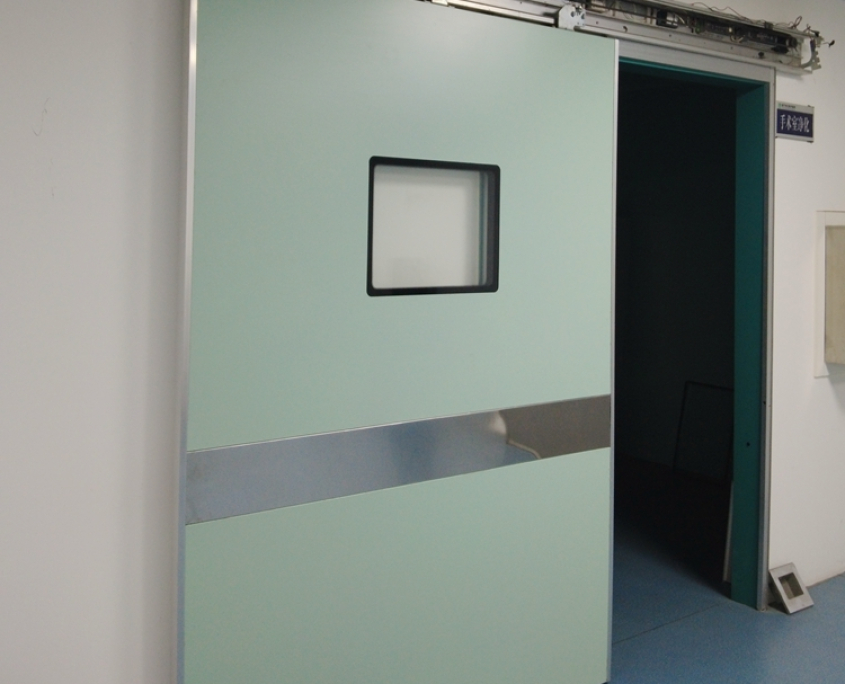
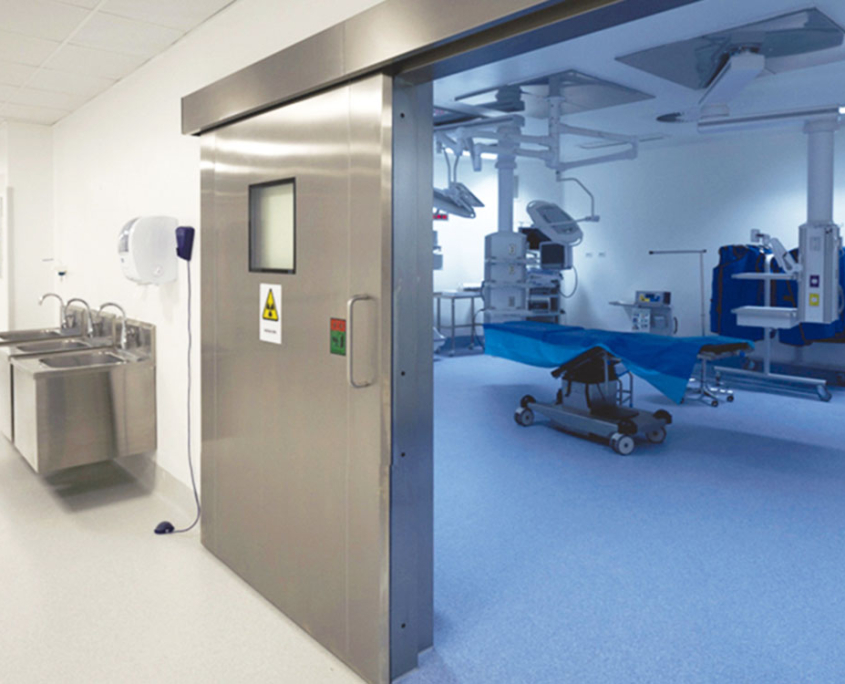
Lead doors are used in hospitals and medical centers, particularly in radiology, CT scan, MRI, and radiology laboratories. Their main purpose is to prevent the spread of ionizing radiation and protect patients, staff, and the surrounding environment.
These doors are typically installed in areas exposed to X-ray or gamma radiation, where they prevent radiation from leaking outside the room.
Advantages
- Protection of staff and patients against ionizing radiation
- Customizable lead thickness and door dimensions
- High durability and strength in hospital environments
- Ability to apply lead shielding to glass doors with stainless steel frames
- Attractive design compatible with hospital interiors
Safety Notes
- The lead thickness and design must be chosen according to the type and intensity of radiation.
- Radiation leakage testing after installation is essential.
- Maintenance and cleaning should use appropriate materials to prevent corrosion and damage to the door surface.
Structure and Features
Internal Lead Layer:
- The thickness of the lead layer varies depending on the radiation energy and protection standards.
- Usually between 1 to 3 mm, but can be thicker in special cases.
Frame and Body:
- The body is made of durable 304 stainless steel.
- It is also possible to apply lead shielding to glass doors with a stainless steel frame to ensure full protection.
- Lock and Handle Mechanism:
- Handles and locks are designed to ensure the door closes completely, preventing any radiation leakage.
- Some models include automatic systems and sensors to detect door closure.
Dimensions and Installation:
- Doors can be single or double leaf, with standard or custom heights and widths.
- Installation must be precise and follow standard clearances to ensure maximum protection.